Choosing a CNC machining supplier isn’t only about getting the lowest quote. When your product relies on tight tolerances, certified materials, and consistent quality, the wrong supplier can lead to rework, delays, supply chain disruptions, and long-term financial loss.
This comprehensive guide explains how to evaluate, audit, and select a CNC machining supplier using a structured scoring method. It includes technical, commercial, and quality criteria used by top engineering teams in Europe and North America — plus a downloadable checklist you can apply to your next RFQ shortlist.
Quick Supplier Scorecard
If you need a short version before going deeper, use this 5-pillar supplier scorecard:
1. Quality & Certifications
ISO 9001, IATF-16949, AS9100, traceability, PPAP, First Article Inspection (FAI).
2. Technical Capabilities
3-axis / 4-axis / 5-axis machining, Swiss turning, complex milling, multi-axis programming, CAD/CAM support.
3. Inspection and Metrology
CMM, optical measurement, surface roughness testing, batch inspection strategy, inspection reports.
4. Engineering Support & DFM
Free DFM review, tolerance optimization, material recommendations, proactive manufacturability suggestions.
5. Lead Time, Flexibility & Communication
Realistic delivery times, prototyping speed, scalability to small/large batches, response time in <24 hours.
You’ll find the expanded, detailed checklist below.
Why Choosing the Right CNC Machining Supplier Matters
Selecting a CNC machining partner is a strategic decision because it directly affects:
1. Quality Risk
Precision parts with tight tolerances (±0.01–0.02 mm) require stable processes, calibrated equipment, and experienced machinists. A supplier lacking these capabilities introduces:
· dimensional inconsistency
· poor surface finish
· material defects
· out-of-tolerance functional features
2. Compliance & Industry Requirements
Different industries have mandatory certification expectations:
· Aerospace: AS9100
· Automotive: IATF-16949
· Medical: ISO 13485
· General industry: ISO 9001
Working with non-certified suppliers may block your product from entering regulated markets.
3. Supply Chain Stability
The wrong CNC partner can cause:
· delayed product launches
· unexpected cost increases
· batch-to-batch inconsistency
· shipping issues
· inability to support urgent orders or engineering changes
4. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
The cheapest quote often becomes the most expensive decision. Rework, scrap, returns, and production line delays outweigh initial savings.
Step 1 — Define Your Technical & Program Requirements
Before you evaluate suppliers, define your project internally. Without clarity, suppliers will quote with assumptions, increasing the risk of mismatches.
Your Specification Checklist
✔ Material
Aluminum (6061/7075), stainless steel (303/304/316), alloy steel, brass, copper, titanium, PEEK, PC, ABS, nylon…
✔ Tolerances
· General tolerances (ISO 2768-m, f, c)
· Critical tolerances (±0.01, ±0.005, GD&T features)
✔ Key features
Deep blind holes, thin walls, micro features, complex surfaces, threaded holes, press-fit areas.
✔ Surface finish
Ra level, anodizing, bead blasting, electroplating, powder coating, passivation.
✔ Quantity & Order Type
Prototype, bridge production, low volume, mass production.
✔ Inspection Requirements
FAI, CMM reports, full QA reports, material certificates (MTR).
Why this step matters
Suppliers cannot provide accurate pricing or assess manufacturability without complete specifications. Clear data enables you to compare apples to apples.
Step 2 — Evaluate Technical Capabilities
A CNC supplier’s machinery, tooling, and engineering capability determine whether they can meet your part complexity.
Key Technical Indicators
1. Machine Types & Capacity
Evaluate the type and number of machines:
· 3-axis CNC milling
· 4-axis indexing machining
· 5-axis machining centers
· CNC Swiss turning
· Multi-tasking mill-turn machines
High-complexity parts typically require:
· 4-axis / 5-axis centers
· Mill-turn combos
· Tight thermal stability
· High-precision spindles
2. Software & Programming
Check whether the supplier uses professional CAD/CAM systems:
· Mastercam
· SolidWorks CAM
· UG / Siemens NX
· Fusion 360
· HyperMill
Advanced CAM enables optimized toolpaths, shorter cycle times, and better surface finish.
3. Materials Expertise
Some suppliers only handle aluminum. Others specialize in stainless steel, titanium, or engineering plastics.
Match your material to the supplier’s core experience to avoid machining defects.
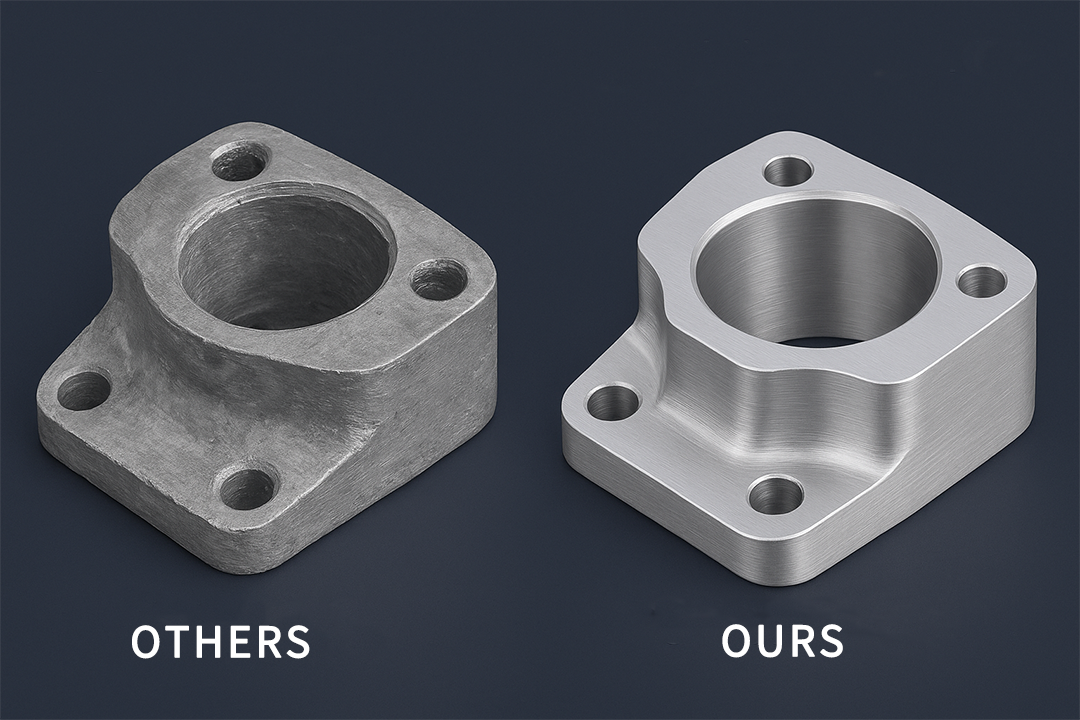
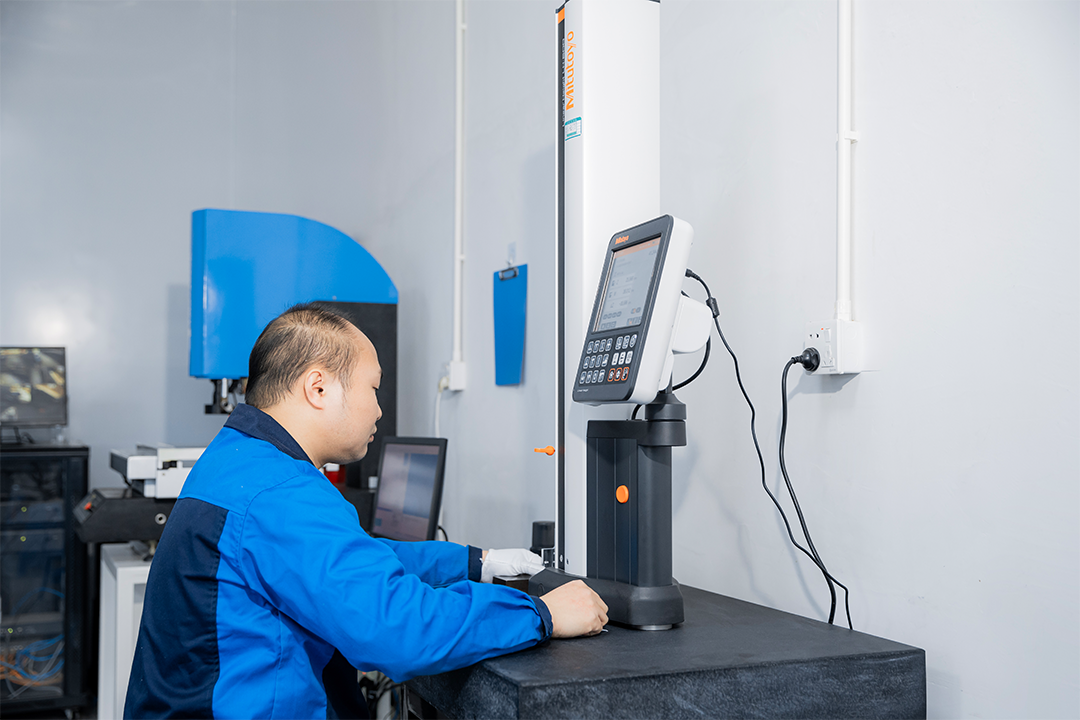
Step 3 — Assess Quality Control & Inspection Capabilities
Quality is the most important factor when selecting a CNC machining supplier.
Inspection Infrastructure to Look For
1. Metrology Equipment
At minimum, a professional supplier should have:
· CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine)
· Height gauges
· Optical vision measurement
· Pin gauges, thread gauges, block gauges
· Profilometers for surface roughness
2. Quality Certifications
Ask for copies of:
· ISO 9001
· IATF-16949 (automotive)
· AS9100 (aerospace)
· ISO 13485 (medical)
A certified quality system ensures traceability and consistency.
3. Inspection Process
Confirm they provide:
· Incoming material inspection with MTR
· In-process inspection
· Final inspection
· Full dimensional report if needed
· PPAP or FAI for critical applications
4. Traceability
A strong supplier can provide:
· batch traceability
· tool life tracking
· machine calibration records
· operator responsibility documentation
If traceability is missing, you risk batch inconsistencies.
Step 4 — Evaluate Engineering Support & DFM Capability
The best CNC suppliers are not simple “machining vendors”—they are engineering partners.
What good DFM support looks like
· Suggesting tolerance relaxation where possible
· Identifying manufacturability issues before machining
· Proposing material alternatives
· Improving strength, flatness, or cosmetic appearance
· Offering assembly-fit suggestions
· Notifying potential deformation risks
A supplier with strong DFM capabilities can help you:
· reduce machining cost by 10%–40%
· improve part performance
· avoid redesign cycles
If a supplier never questions your drawings, that’s a red flag.
Step 5 — Communication, Responsiveness & Project Management
Engineering projects depend on smooth communication. You should evaluate:
1. Response Speed
Professional suppliers typically respond:
· RFQs: within 12–24 hours
· Technical questions: within the same day
· DFM feedback: within 1–2 days
2. Transparency
Look for suppliers who provide:
· clear breakdown of pricing
· realistic, not over-promised lead times
· proactive risk warnings
· regular production updates
3. Project Management Tools
Advanced suppliers may use:
· ERP / MES systems
· Real-time job tracking
· Digital work orders
· Internal QC dashboards
These systems dramatically improve reliability.
Step 6 — Lead Time, Capacity & Flexibility
Fast lead time is useless if it’s not realistic. Evaluate:
1. Production Capacity
Ask:
· How many CNC machines?
· What is the average machine utilization rate?
· What is the bottleneck station (e.g., CMM)?
· Can they scale from prototype to mass production?
2. Lead Time Reliability
Typical CNC lead times:
· Prototype: 3–7 days
· Low volume: 7–15 days
· Complex 5-axis parts: 10–25 days
Suppliers with in-house surface finishing (anodizing, polishing, coating) can deliver much faster.
3. Flexibility
True partners support:
· urgent orders
· engineering changes
· batch schedule adjustments
· inventory storage (VMI)
Flexibility is a competitive advantage.
Step 7 — Pricing, Quotation Transparency & Total Cost of Ownership
Price is important — but total cost includes much more.
What to evaluate
1. Quotation Depth
Look for:
· detailed process descriptions (milling, turning, tapping, finishing)
· material cost breakdown
· tooling cost (if any)
· finishing cost
· shipping cost
· inspection cost
Transparent suppliers are more reliable.
2. Cost vs Performance Balance
The cheapest option often:
· uses uncertified materials
· outsources machining
· lacks QC
· causes rework or quality issues
Always evaluate based on total lifetime cost.
Step 8 — Review Real Samples, Case Studies & Customer Feedback
A qualified CNC machining supplier should provide:
· sample parts
· case studies from similar industries
· testimonials from engineering teams
· references upon request
Sample inspection checklist:
· dimensional accuracy
· surface finish quality
· burr removal
· coating/anodizing consistency
· packaging quality
These details reflect how the supplier treats your actual orders.
Step 9 — Supply Chain, Logistics & Packaging
Global buyers should check:
1. Shipping Capabilities
Does the supplier offer:
· air freight
· express freight
· DDP (duty paid)
· customs handling assistance
2. Packaging Quality
Strong suppliers use:
· anti-scratch film
· foam compartments
· vacuum packaging
· custom labels
· moisture protection
Great packaging reduces damage risk to near zero.
Step 10 — Final Supplier Selection: Build a Scoring Matrix
Use a weighted scorecard to make a fair comparison.
Example weights:
|
Category |
Weight |
|
Quality & Certifications |
25% |
|
Technical Capability |
20% |
|
Inspection & QC |
15% |
|
DFM & Engineering |
15% |
|
Lead Time & Capacity |
10% |
|
Communication |
10% |
|
Price |
5% |
This model avoids the common mistake of choosing based on price alone.
Conclusion — What Makes a CNC Machining Supplier Truly Reliable
A great CNC machining partner combines:
✔ strong engineering
✔ predictable QC
✔ transparent communication
✔ consistent lead time
✔ competitive pricing
✔ willingness to grow with your project
By following the above 10-step method, you can significantly reduce sourcing risk, improve product quality, and build a long-term relationship with a trusted supplier.
Want Help Choosing the Right CNC Supplier? Let Us Quote & Provide DFM Feedback”
FAQs (SEO-optimized)
Q1. What is the most important factor when choosing a CNC machining supplier?
Quality control and consistency — not price — is the most critical factor.
Q2. How do I reduce machining cost without compromising quality?
Optimize tolerances, choose machinable materials, and work with a supplier that provides DFM feedback.
Q3. How can I verify a supplier’s capability remotely?
Request a video factory tour, real-time machine list, sample reports, certifications, and sample parts.
Q4. Should I choose a supplier with 5-axis machines?
If your parts involve complex surfaces, undercuts, or multiple setups, yes — 5-axis greatly improves accuracy.
Post time: Nov-26-2025